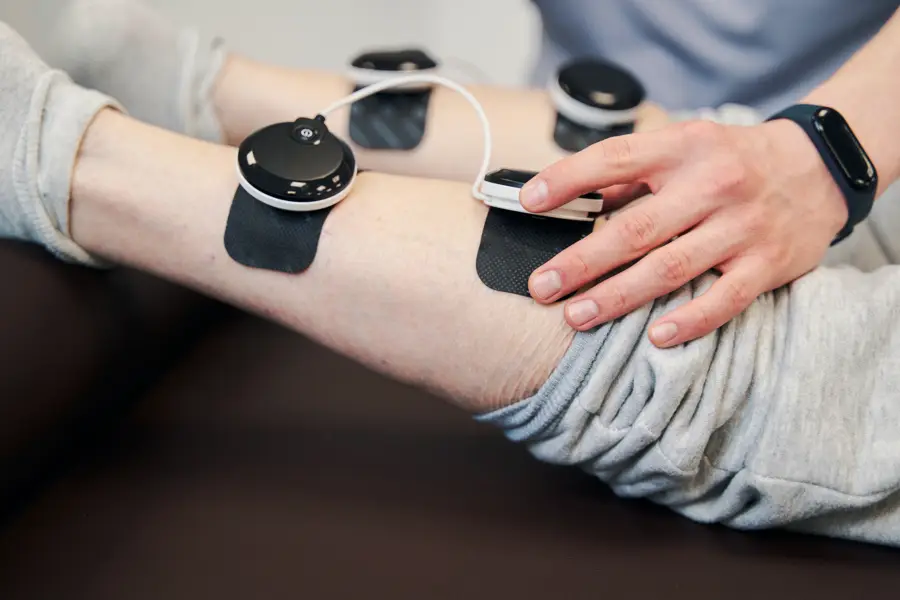
Peripheral Neuropathy / Nerve Pain
What is Peripheral Neuropathy / Nerve Pain?
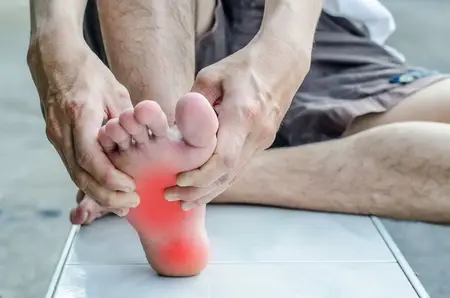
Peripheral neuropathy refers to the various conditions that result when nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord from and to the rest of the body are damaged or diseased. This damage interferes with the nerves’ normal functioning, causing symptoms such as pain, tingling, and muscle weakness.

What are signs & symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy / Nerve Pain?
- Extreme temperatures intolerance
- Tingling or numbness in the extremities
- Sharp or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness or wasting
- Paralysis if motor nerves are affected
- Problems with coordination and balance
- Problems with bowel, bladder, or digestive functions
- Chronic pain in local area or multiple areas